CloudFlare Boosts Millions of Users Over China’s Great Firewall
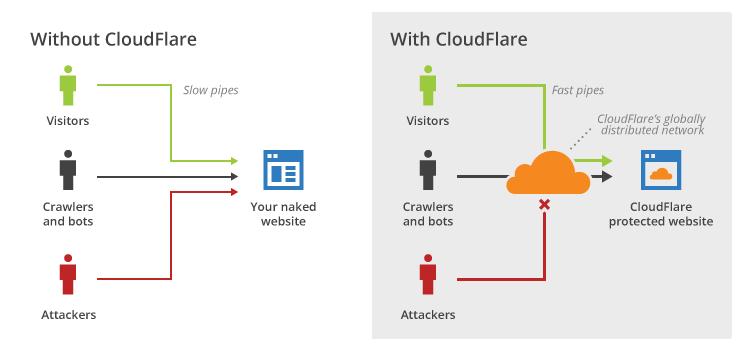
San Francisco based startup CloudFlare is well on its way to revolutionizing the Internet, with a little help from Solarflare. Utilized by over 2,000,000 sites and counting, CloudFlare accelerates, optimizes, and protects websites, leading to 50% faster load times while using 60% less bandwidth. They also block threats and limit abusive bots from interfering with site performance, making it a win-win for business owners and customers alike.
CloudFlare’s goal of wanting to power and protect the entire Internet is an ambitious one, but they’re well on their way, already processing over a trillion requests per month through their network. This is why CloudFlare turned to Solarflare for their server solutions, needing a 10 GbE capable of keeping pace with their massive growth and rapid-fire networking needs. Solarflare 10GbE Onload has stepped up the plate to deliver the lowest latency, highest performance, and most scalable solution to enhance CloudFlare’s quest to improve the Internet for businesses and individuals around the world. Cloudflare Software Engineer Marek Majkowski recently called Solarflare’s OpenOnload a “magical network accelerator” for its kernal bypass abilities.
A recent New York Times article highlights how CloudFlare is already making huge strides in making the internet a faster, safer, and more secure place to do business. Tackling one of the most difficult areas on the planet to get reliable Internet service, CloudFlare recently partnered with Baidu—China’s equivalent of Google. In a new kind of partnership that will set the precedent for the industry, CloudFlare has paired its web traffic technology with Baidu’s data center network to empower an Internet super highway in China. Billions of users who were once hindered by the so-called “Great Firewall” are now experiencing super fast load times thanks to CloudFlare and Baidu’s virtual joint venture. Foreign sites are more easily accessible in China now thanks to a unified network, which also allows Chinese sites to run in destinations outside the country. Since the fast-lane began operating last December, CloudFlare and Baidu said they have registered 450,000 businesses, accounting for 57 billion page views per month.
An even more impressive figure: both companies estimated that over a period of 24 hours on Wednesday, their service saved about 243 years in time that Chinese users would’ve spent waiting for pages to download!
Solarflare is proud to partner with a startup nimble enough to zip over the Great Firewall of China millions of times a day. CloudFlare will be an exciting online security company to watch as they continue to change the way people around the world use the Internet, safely and speedily.
How Solarflare’s Middleware Accelerates Applications
From high frequency trading to weather modeling, an ever-increasing number of industries are coming to rely on high performance computing to transmit real-time complex data swiftly and securely. Improving and accelerating application performance is a key piece of this puzzle, and Solarflare’s innovative middleware solutions address this issue with ease.
Solarflare’s OpenOnload is a Linux-based, Open Source high-performance application accelerator that delivers lower and more predictable latency and higher message rates for TCP and UDP-based applications.This bundled service and support is suitable for deployment in Fortune 1000 data centers, high-frequency trading applications, and HPC applications. This middleware solution significantly enhances application performance by improving network I/O latency, bandwidth, and message rates, while reducing CPU utilization. Best of all, EnterpriseOnload does all this without needing to modify applications or change the network infrastructure.
The stats speak for themselves:
- TCP and UDP acceleration including multicast
- Lowest application-to-application latency (½ round-trip)
- Up to 3 million messages per second on a single CPU core
- Binary compatible BSD sockets API
- No application modifications or network upgrades required
Two of OpenOnload’s best features:
1. Socket caching: This feature allows OpenOnload to cache file descriptors and filters to system calls into the OS for each new socket created. For applications with a high rate of incoming connections (e.g. web servers and other similar use cases) this feature translates into large increases in achievable connection rate and moves OpenOnload well beyond the performance of the native kernel network stack for applications with high connection rates.
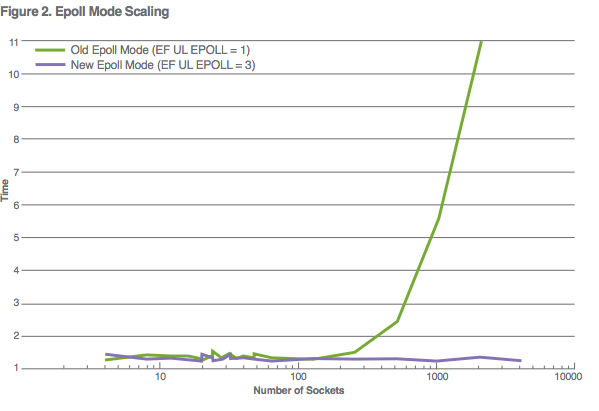
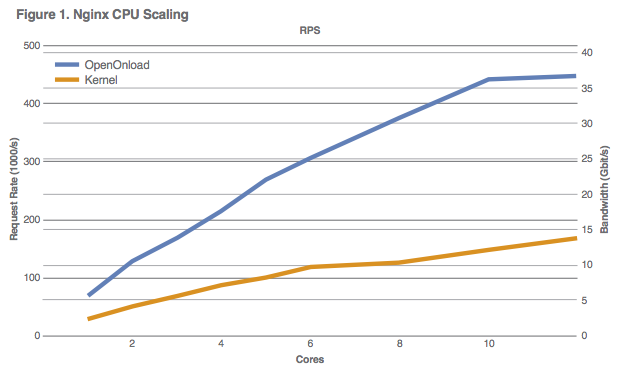 2. Epoll Mode Scaling: The scalable epoll mode scales linearly rather than in proportion to the size of the epoll set. For large epoll sets this translates to a big improvement in performance and scalability, as shown in Figure 2 below.
2. Epoll Mode Scaling: The scalable epoll mode scales linearly rather than in proportion to the size of the epoll set. For large epoll sets this translates to a big improvement in performance and scalability, as shown in Figure 2 below.
Implementing better middleware is a surefire way to improve application performance across the server, and OpenOnload delivers the kind of results that HPC-reliant companies need.

Why Solarflare’s Packet Capture Tech Provides the Best Network Security
According to the tech research firm Gartner, more than 25 billion things will be connected to the Internet by 2020. This massive Internet of Things presents amazing opportunities for innovation in how we go about every area of our lives, from the ability to control a home thermostat from thousands of miles away to trading large shares of stock with the effortless swipe of a screen. This unprecedented amount of connectivity also means we need to amp up our online security measures in real ways. With billions of devices now transporting data, it’s essential that companies protect their assets and their customers with stringent security measures.
The number one area of network infiltration happens at the server level through these 4 main types of attacks: zero-day, cache poisoning, denial of service (DoS) and distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks. While these hacks can be mitigated through various precautions, a company’s best line of defense is in implementing low latency, high-frequency packet capture solutions to increase security not only on the perimeter, but at the top of every rack or within every server.
 Solarflare approaches network security in a realistic way by assuming that attacks will happen- it’s a real side effect of the times in which we live. But instead of letting an intruder have access to the entire castle just because they crossed the moat, Solarflare’s packet capture approach adds a new layer of protection at the server level. Think of it as a series of safes, locking your valuables up separately to prevent unwelcome visitors from running off with all the crown jewels.
Solarflare approaches network security in a realistic way by assuming that attacks will happen- it’s a real side effect of the times in which we live. But instead of letting an intruder have access to the entire castle just because they crossed the moat, Solarflare’s packet capture approach adds a new layer of protection at the server level. Think of it as a series of safes, locking your valuables up separately to prevent unwelcome visitors from running off with all the crown jewels.
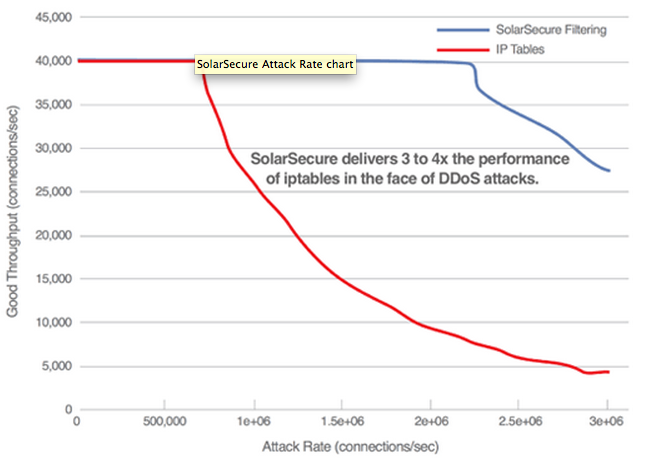
The core of Solarflare’s DDoS attack mitigation consists of a high performance packet filter engine that uses a pseudo-microcode instruction set to configure the filter engine to selectively accept, reject or rate-limit packets based on packet headers and packet contents. The microcode used for filtering is under user control, making the filtering behavior highly configurable. This packet capture approach allows “bad” traffic to be detected very early in the network stack, so DDoS attacks can be absorbed without degradation of “good” traffic. The filter engine provides the ability to efficiently block or rate limit packets based on their contents, as well as request level deep packet inspection. For example, HTTP requests can be inspected and connections aborted dependent on the contents of the HTTP headers.
In the face of DDoS attacks, servers enabled with the SolarSecure Filter Engine were found to be 3 to 4 times more effective at packet filtering than iptables. It’s pretty clear that the future of network security is in this multi-layered packet capture approach.

SolarFlare’s Ethernet Solutions Power the Future of Nuclear Fusion
Among the many exciting innovations taking place across a wide array of industries where Solarflare’s networking solutions are implemented, the cutting edge research being done at the Princeton Plasma Physics Lab (PPPL) truly has the power to change the world.
Nuclear fusion is the energy that powers the stars and the sun, and scientists have been working toward harnessing this power for decades. So it’s exciting that PPPL, joined by the worldwide fusion energy research community, is working to develop the first self-sustaining fusion reactor with a slated date for completion of 2016. While the physics behind achieving such a goal is complex, on a simplified level researchers are modeling the properties of how deuterium and tritium (hydrogen isotopes) move in a plasma field, which is essential to sustained fusion reaction. In addition to producing helium, this collision produces a huge amount of energy: up to 450 times the input energy to fuel the reaction. Fusion is a promising method of energy conversion because of its inexhaustible low-cost fuel supply, absence of global warming side effects, and low risk of reactor meltdown.
Today fusion reactions stop operating after a short period, but the goal is to create a fully sustainable fusion reactor that would be able to operate for long periods of time, sustained only by the addition of more hydrogen to the reaction.This point where nuclear fusion becomes self-sustaining is called ignition, and recent strides made by the Princeton Plasma Physics Lab take us one step closer to igniting this long-time energy dream into a viable reality. Researchers at PPPL recently confirmed a novel way to harness the rotation of hot charged plasma gas within fusion facilities. Read more about the physics behind this exciting step toward ignition at Princeton Plasma Physics Lab’s website.
Research simulating the fusion process requires a huge shared compute cluster capable of running over 230,000 simulation jobs a year. These simulations occur at universities all over the world and are then shared with members of the fusion energy research community. Highly parallelized models require several thousand CPU cores per job, and simulations can run for up to weeks at a time. So it goes without saying that saving even 3% on run times accelerates research significantly.
Tests at PPPL determined that using SolarFlare’s 10GB Ethernet networking software and hardware—the industry leader in ultra-high performance, ultra-low latency networking—rather than DDR InfiniBand improved cluster performance and speed by 36%. This startling result implies that 10GbE can be a useful interconnect not only for GYRO, but also for any stepwise iterative code in other physical modeling fields, such as Genomics, Computational Fluid Dynamics, and Finite Element Analysis. At any rate, the strides being made in nuclear reaction research as a viable energy source makes this an exciting time to be alive.
Image credit: Anita Gould

Avalanche’s Magnetic Memory will Revolutionize Technology
Every computer system, storage unit, and mobile device in existence today all have one thing in common: the need for memory. From performance to scalability to security, strong and reliable memory is essential to the success of any unit of technology today. Until now, the memory market has been dominated by existing technologies including charge-based, volatile memories (DRAM and SRAM) and non-volatile memories (NOR and NAND flash). These technologies have successfully existed for 30 years, but are they best suited for the changing needs of future IT infrastructure, which come with increasing demands for more speed, reliability, and lower costs? Avalanche Technology, a leader in disruptive technology, has a better solution.
The first in the industry to do so, Avalanche Technology has successfully developed a new form of memory technology called Spin Transfer Torque Magnetic Ram (STT-MRAM). This is an exciting leap into the future of memory solutions. Avalanche’s STT-MRAM is a high-speed non-volatile magnetic memory based on proprietary perpendicular magnetic tunnel junction (pMTJ) cells manufactured on high volume, low cost, standard CMOS 300mm process. As such, Avalanche’s STT-MRAM is a well suited and commercially viable memory replacement for many embedded and/or stand-alone DRAM and SRAM applications, including data storage, mobile, wearable devices, and networking equipment. STT-MRAM combines the best features of today’s dominant memory technologies with the added benefits of scalability beyond 10nm node, unlimited endurance, and the low power and low cost of flash memory.
Avalanche’s new technology has huge market opportunities, particularly as a storage technology, due to its speed and endurance. Moving from volatile memories such as SRAM and DRAM to a non-volatile memory architecture like STT-MRAM will improve memory systems across a wide range of industries and applications. Since it is non-volatile, STT-MRAM will retain its data when power is lost or is turned off—a huge bonus for large scale storage systems.
In an interview with EETimes, former VP of business development Michael Ofstedahl said that Avalanche had remained quiet about its technology until it had been developed into a commercially viable solution. The recent success of Avalanche’s STT-MRAM chip testing proves that it’s just a matter of time before we see systems implementing this new superior non-volatile memory technology. As this new memory is based on pMTJ cells manufactured on a high volume, low cost, standard CMOS 300mm process, it’s a better solution for high-volume, cost-sensitive applications than the industry’s current magnetic memory solutions. For a more in-depth explanation of the components of Avalanche’s STT-MRAM, check out the full EETimes article here.
Research firm Coughlin Associates sees enormous potential in Avalanche’s new technology. According to their recent report, a huge boom in STT-MRAM is predicted through 2019. By storing data without requiring power to be maintained to the circuits, the annual MRAM and STT-MRAM revenues will skyrocket from about $190 million in 2013 to $2.1 billion by 2019. The report also predicts the demand for standalone MRAM components and embedded MRAM will drive a market for MRAM manufacturing equipment to upwards of $245 million by 2019. While this is only the beginning for Avalanche Technology’s STT-MRAM, it’s an exciting time for the memory industry and an opportunity for limitless innovation for technology across the board, from mobile to data storage and beyond.
image via Flickr/pympym

International Hacking Sting Highlights Need for Stronger Network Security
Cyber security is among the top threats to the financial industry, as a glance at the news headlines will confirm. Just this week, a large-scale insider trading scheme, replete with a network of international hackers, was brought to justice by federal prosecutors and SEC regulators with a series of arrests and indictments. Called the most sophisticated fraud scheme combining cyber hacking with securities fraud in history, in total 32 rogue traders hackers reaped over $100 million in illegal proceeds in this five-year fraud. The scheme involved thousands of stolen corporate news releases, requested by traders operating out of their homes in suburban America, and illegally obtained by a group of Eastern European hackers. The stolen news reports, which came from sources such as PR Newswire, were then used to trade on news before it was made public. Paul J. Fishman, U.S. Attorney for the District of New Jersey, stated that the wire services were not at fault, and had cooperated completely in the ongoing investigation.
As hacking schemes become increasingly sophisticated, so too does the need for companies to step up their cyber security measures. Companies would do well to proactively employ layered network protection to safeguard both customer and company assets. Solarflare’s President and CEO Russell Stern recently sat down with TabbFORUM to discuss the challenges of protecting sensitive financial data from hackers—a topic that’s increasingly relevant with each emerging headline about this latest hacking ring. Stern shared a 3-step plan for large corporations to safeguard sensitive data through early breach detection and prevention. Check out the full interview here.
3 Steps to Building a More Secure Network:
1. Start at the network server: the network server is the #1 target of all cyber attacks. Your best line of defense against hacking is a strong network server, like Solarflare’s SolarSecure Filter Engine, which utilizes a high performance packet filter to enable “bad” traffic to be detected very early in the network stack, so DDoS attacks can be absorbed without degradation of “good” traffic.
2. Build layered defenses: Combining live threat intelligence with real-time updates provides another strong layer of defense. This approach assumes breaches will happen, but the layers of defense will cause the attack to slow down enough to be detected and corrected. Solarflare’s I/O Adapters are the leader in low latency high frequency server solutions for high performance computing.
3. Close the gap: Future threat mitigation strategies for financial service organizations will continue to fill in the gap between detecting breaches, preventing them, and preventing the exfiltration of sensitive assets from the servers. Firms should use these strategies to help mitigate costs of prevention and shorten the time frame to detection, thereby creating a cost-effective and powerful security solution.
Image via Flickr/Dennis Skley

Canada’s New Stock Exchange Aims to Reshape Capital Markets
Toronto based Aequitas NEO Exchange, launched this past April, is on a mission to reshape capital markets and bring Canadians’ trust—and their investments—back to the core mission of how exchanges should operate. Namely, to provide a mutually beneficial marketplace in which investors looking to expand their portfolios can pair with companies looking to gain capital. Funding in turn fuels more jobs, more prosperity, and more growth: all great things that keep the cycle running smoothly. But certain practices have disrupted this cycle, especially in the digital age. Chief among these offensive practices, according to NEO President and CEO Jos Schmitt, is predatory high frequency trading.
While high frequency trading depends on information transferred in fractions of a second made possible by advances in networking, the practice of using technology to make money goes back to 18th century enterprising banker Nathan Mayer Rothschild, who used carrier pigeons to make his fortune. Legend has it Rothschild learned the outcome of the Battle of Waterloo before anyone else by having the info sent via carrier pigeon, allowing him to use news of Napoleon’s defeat to snatch up government bonds before other bankers had the chance.
NEO’s President believes that unfair advantages have been skewed in the modern-day carrier pigeon equivalent of high frequency trading. His goal of creating a more transparent, fair market system has already spurred Toronto Stock Exchange—owned by for-profit corporation, TMX Group Inc.—to digitally regulate high frequency trading. Because exchanges thrive off high volume trading, high frequency practices have been allowed to flourish in the past. NEO hopes to curtail unfair practices entirely through greater governance. Rather than being publically owned, the NEO Exchange is run by investors and issuers, including OMERS Capital Market and Barclays Corp. All hold an equal share—thereby eliminating the frenzy to deliver high trade volume value to shareholders.
NEO by the Numbers:
61 million shares (value of $1,103 million) shares traded week of 7/20/15
Average trade size of 336, representing a 1.8% market share (2.7% in traded value)
To fuel these kinds of powerful changes, NEO required a powerful server solution. Prior to launch, they chose to implement Solarflare’s 10 Gigabit Ethernet networking software and hardware—the industry leader in ultra-high performance , ultra-low latency networking—to support its high trading volumes. Along with deploying I/O adapters, the NEO Exchange will implement Solarflare’s advanced Precision Time Stamping software. Nowhere is precise time stamping more critical in accurately recording network activity than in financial markets. Solarflare is the only company offering 10GbE PTP server adapter with a Stratum 3 clock, increasing accuracy from milliseconds to microseconds. Implementing these technologies into NEO’s framework is an essential step in helping its leaders achieve their goal of creating a new kind of national stock exchange that elevates transparency and fairness to the highest levels.
Image: Flickr/Om

United Airlines Rewards Hackers with Frequent Flier Miles
United Airlines recently rewarded two hackers for finding security breaches in the airline’s computer system by giving them each one million frequent-flier miles. Wait, isn’t hacking a bad thing? Should incentives be used to dissuade hackers—or should companies be proactively adopting higher security measures within the network to protect customer and company assets?
Setting a new precedent for the transportation industry, United recently hosted a “bug bounty” award for computer programmers to identify possible security breaches in company infrastructure before a “real” hacker has the chance to do so. It’s an incentive driven way for companies to enlist the hacking expertise of coders who are looking not to steal a bunch of classified information, but to cash in on some pretty hefty prizes. United’s contest promised rewards on a tier system: bugs identified in third-party structures would receive 50,000 miles in compensation, exploits that could compromise customer information earned 250,000 miles, and major remote-code execution flaws would earn so called “white hat hackers” the jackpot prize of 1,000,000 frequent-flier miles.
By adopting the bug bounty competition method, United received valuable information about fortifying its online security measures before that information could get into the wrong hands. And while a million frequent flier miles can get you around the world five times over, awarding that kind of life-changing prize isn’t costing United much of anything. It’s a win-win for United in terms of forward thinking publicity, and a win for coders who’ve caught the travel bug.
The bug bounty model was first conceived by engineer Jarrett Ridlinghafer in 1996, when he was working at Netscape Communications. Based on Netscape’s success in leveraging coding expertise through this new model of incentives, tech giants including Facebook and Google quickly followed suit. United Airlines is the first in the airline and transportation industry to extend a similar offer to white hat hackers. One of the winners, Jordan Wiens of Florida, had never entered a bug bounty competition before, and considered the hacks he identified as minor in nature. Imagine his surprise when he won the 1,000,000 miles, not to mention some good publicity for his online security company, Vector35.
In the future, we can expect to see a growing trend of companies rewarding programmers who expose their system flaws for rewards. It sure beats the alternative outcome that we’ve seen in recent months at companies like Home Depot and Target. A far better solution would be for more companies to proactively adopt higher security measures within the network to protect customer and company assets, like those offered by SolarFlare. Integrated into network servers – usually the primary target of cyber attacks – the SolarSecure Filter Engine mitigates attacks with a high performance packet filter engine, allowing for a higher degree of monitoring and securing data without having to add additional hardware. The better a company’s ultimate line of defense against potential hackers, the better its customers will feel about their cyber security.
Images via Flickr/elhombredenegro;SolarFlare